If you’re curious about what exactly sole custody means, you’ve come to the right place! Sole custody is a term that often comes up in legal discussions related to child custody. It refers to a situation where one parent has been granted exclusive legal and physical custody of a child. In other words, it means that one parent has the sole authority to make important decisions regarding the child’s upbringing and is responsible for their day-to-day care. Let’s delve deeper into the intricacies of sole custody and understand what it entails.
When it comes to determining sole custody, courts consider various factors such as the child’s best interests, the ability of each parent to provide a stable and nurturing environment, and any history of abuse or neglect. Sole custody can be granted in cases where one parent is deemed unfit or unable to fulfill their parental responsibilities adequately. It’s important to note that sole custody does not completely eliminate the non-custodial parent’s rights. They may still have visitation rights or be granted supervised visitation in certain circumstances. Understanding the concept of sole custody is crucial, as it has significant implications for the child and parents involved. So, let’s explore this topic further and gain a comprehensive understanding of what sole custody truly means.
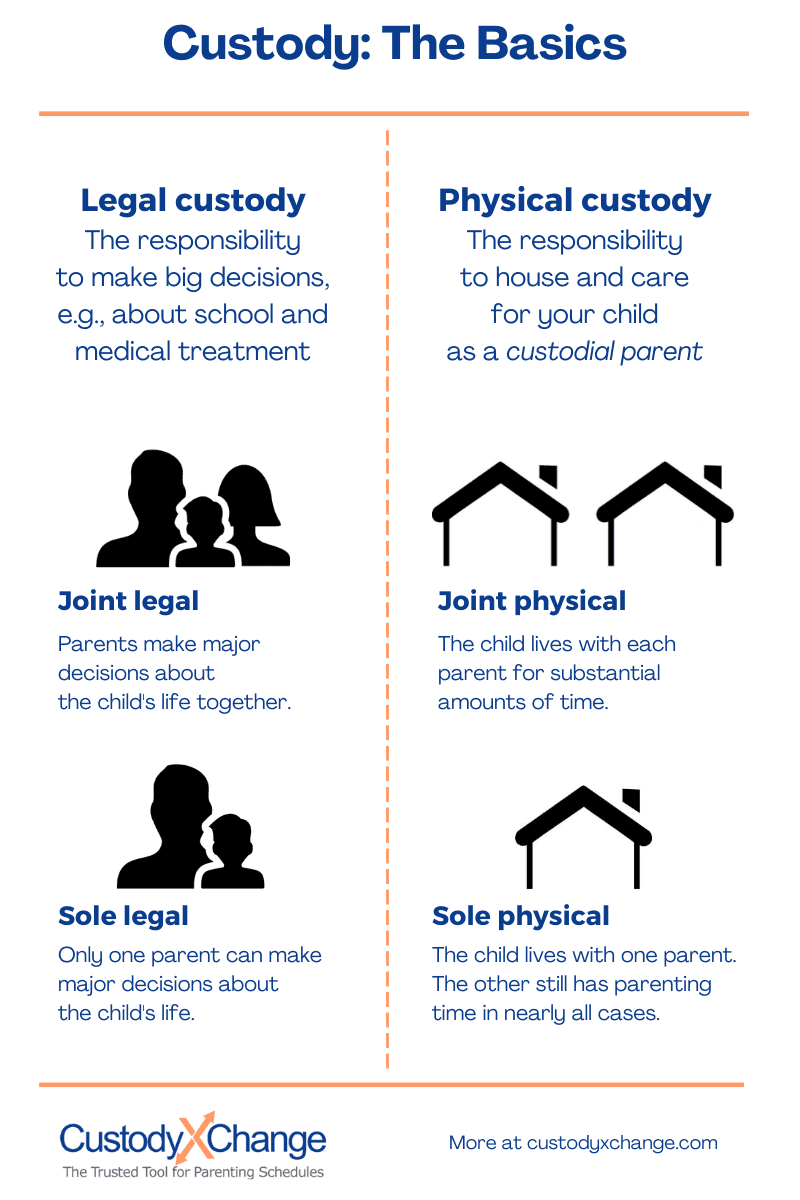
Sole custody is a legal arrangement where one parent has full custody and control over a child. In this type of custody, the parent with sole custody has the authority to make all major decisions regarding the child’s upbringing, including education, healthcare, and religious matters. The other parent, known as the non-custodial parent, may still have visitation rights, but they do not have the same decision-making power. Sole custody is typically awarded when it is deemed to be in the best interests of the child.
Understanding Sole Custody: A Comprehensive Guide
Sole custody is a legal arrangement in which one parent is granted exclusive rights and responsibilities for the care and upbringing of a child. This means that the parent with sole custody has the authority to make decisions about the child’s education, healthcare, and general welfare, without the need for input or agreement from the other parent. In this article, we will delve into the details of what sole custody entails, the reasons why it may be awarded, and the potential impact it can have on both parents and children.
What Does Sole Custody Entail?
When a court grants sole custody to one parent, it means that the other parent is usually limited to visitation rights or, in some cases, no contact at all. The parent with sole custody becomes the primary custodial parent and is responsible for providing the child with a stable and nurturing environment. This includes making important decisions regarding the child’s education, healthcare, religious upbringing, and extracurricular activities.
Sole custody can be awarded in cases where there is evidence of abuse, neglect, or substance abuse by one parent, or if the court determines that it is in the best interests of the child to have limited or no contact with the other parent. It is important to note that sole custody does not necessarily mean that the non-custodial parent is unfit or unable to care for the child, but rather that the court has determined that it is in the child’s best interests to have one parent with exclusive decision-making authority.
Reasons for Granting Sole Custody
There are several reasons why a court may grant sole custody to one parent. These reasons typically revolve around the best interests of the child and ensuring their safety and well-being. Some common reasons include:
- Physical or emotional abuse by one parent towards the child
- A history of neglect or abandonment
- Drug or alcohol addiction that poses a risk to the child’s safety
- Domestic violence within the household
It is important to note that the court’s primary concern is the child’s welfare, and any decisions regarding custody are made with this in mind. The court will carefully consider all relevant factors before granting sole custody to one parent.
The Impact of Sole Custody
The granting of sole custody can have a significant impact on both parents and children. For the custodial parent, it means taking on the majority of the responsibilities and decision-making for the child. This can be both rewarding and challenging, as it requires a high level of commitment and dedication. The custodial parent may also face additional stress and pressure, as they are solely responsible for meeting the child’s emotional and physical needs.
For the non-custodial parent, the loss of custodial rights can be emotionally challenging. They may experience feelings of loss, sadness, or resentment. However, it is important for both parents to prioritize the best interests of the child and maintain a cooperative and supportive co-parenting relationship, even in cases of sole custody.
Legal Considerations for Sole Custody
When seeking sole custody, it is essential to consult with an experienced family law attorney who can guide you through the legal process. The court will evaluate various factors, such as the child’s relationship with each parent, the ability of each parent to provide a stable and nurturing environment, and any evidence of abuse or neglect. It is crucial to present a compelling case that demonstrates why sole custody is in the best interests of the child.
It is also important to note that custody arrangements can be modified in the future if circumstances change. If the non-custodial parent can demonstrate that they have made positive changes and can provide a safe and stable environment for the child, the court may consider modifying the custody arrangement to allow for increased visitation or shared custody.
The Benefits of Sole Custody
Sole custody can provide several benefits for both parents and children when it is deemed necessary and in the best interests of the child. Some of the potential benefits include:
- Ensuring the child’s safety and well-being
- Providing stability and consistency in the child’s life
- Allowing for more efficient decision-making
- Reducing conflict between parents
- Protecting the child from potential harm or exposure to unhealthy environments
It is important to remember that each custody case is unique, and the court will make decisions based on the specific circumstances and evidence presented. The ultimate goal is to ensure the child’s best interests are met and that they can thrive in a supportive and loving environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sole custody is a legal arrangement that grants one parent exclusive decision-making authority and responsibilities for a child’s upbringing. It is typically awarded in cases where there is evidence of abuse, neglect, or other factors that pose a risk to the child’s safety and well-being. While sole custody can have a significant impact on both parents and children, the primary focus is always on the best interests of the child. It is important for parents to prioritize effective communication, cooperation, and the well-being of the child, even in cases of sole custody.
Key Takeaways: What is Sole Custody?
- Sole custody refers to a custody arrangement where one parent has legal and physical custody of the child.
- The parent with sole custody makes major decisions for the child without consulting the other parent.
- Sole custody is usually awarded when the court determines it’s in the best interest of the child.
- In sole custody, the non-custodial parent may still have visitation rights, but they don’t have decision-making authority.
- Sole custody can provide stability and consistency for the child but may limit the involvement of the other parent in their life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does sole custody mean?
Sole custody refers to a legal arrangement in which one parent is granted full custody and control over a child, without the involvement or decision-making authority of the other parent. It means that the parent with sole custody has the sole responsibility for making major decisions regarding the child’s upbringing, including matters related to healthcare, education, and religion.
With sole custody, the noncustodial parent typically has limited or no input in decision-making processes, and may only have visitation or parenting time rights as determined by the court. The parent with sole custody has the primary physical and legal responsibility for the child’s welfare.
How is sole custody determined?
The determination of sole custody is typically made by a family court judge based on the best interests of the child. Factors considered in this decision may include the parents’ ability to cooperate, their parenting skills, the child’s relationship with each parent, any history of abuse or neglect, and the child’s preference, depending on their age and maturity.
The court may also consider any evidence or documentation presented by each parent to support their case for sole custody. It is important to note that the court’s decision regarding sole custody can vary depending on the specific circumstances of each case.
What are the advantages of sole custody?
One of the advantages of sole custody is that it provides a sense of stability and consistency for the child. It allows one parent to make decisions without having to consult or negotiate with the other parent, which can lead to a more efficient and streamlined decision-making process.
Sole custody also ensures that the child is not exposed to conflict or tension between the parents, as the noncustodial parent’s involvement is limited. This can create a more peaceful and nurturing environment for the child, promoting their overall well-being.
What are the disadvantages of sole custody?
One of the disadvantages of sole custody is that it places the sole responsibility for the child’s welfare on one parent, which can be overwhelming and challenging, especially when it comes to balancing work and personal life. The parent with sole custody may also face difficulties in making decisions without the input or support of the other parent.
Additionally, sole custody can sometimes result in a strained relationship between the child and the noncustodial parent, as their involvement is limited. It is important for both parents to maintain open lines of communication and work towards a cooperative co-parenting relationship, even in cases of sole custody.
Can sole custody be changed?
Yes, sole custody can be changed under certain circumstances. If there is a significant change in the circumstances of either parent or the child, such as a relocation, a change in the parent’s ability to care for the child, or a change in the child’s needs, a request for a modification of custody can be made to the court.
The court will then evaluate the new circumstances and determine whether a modification is in the best interests of the child. It is important to consult with a family law attorney to understand the specific requirements and procedures for modifying sole custody in your jurisdiction.
What is the Difference Between Primary Custody and Sole Custody?
Final Summary: Understanding Sole Custody
After diving into the concept of sole custody, it’s clear that this legal arrangement plays a crucial role in determining parental responsibilities. By granting one parent exclusive decision-making authority and physical custody over a child, sole custody ensures stability and consistency in their upbringing. While it may seem like a straightforward concept, the intricacies and implications of sole custody are far-reaching.
In conclusion, sole custody is not a decision to be taken lightly. It involves a careful evaluation of the child’s best interests, the parents’ ability to cooperate, and the overall family dynamics. By understanding the significance of sole custody, both parents can navigate the legal process more effectively and prioritize the well-being of their child. Remember, seeking professional advice and support is essential when dealing with custody matters, as it ensures that the final outcome is fair, just, and in the best interest of the child.
