If you find yourself in a dispute or legal conflict, you may have heard about mediation as an alternative to going to court. But what exactly is mediation, and more importantly, is it legally binding? In this article, we will delve into the world of mediation and explore whether the agreements reached through this process hold any legal weight.
Mediation is a process where a neutral third party, known as a mediator, helps facilitate communication and negotiation between parties involved in a dispute. Unlike a judge or arbitrator, a mediator does not make decisions or impose solutions. Instead, they assist the parties in finding a mutually acceptable resolution. But here’s the burning question: Is the outcome of mediation legally binding? Let’s find out!
Mediation is a voluntary process where a neutral third party helps parties in conflict reach a mutually agreeable resolution. While mediation itself is not legally binding, any agreements reached during the process can be legally binding if the parties choose to formalize them. This can be done by drafting a legally binding contract or submitting the agreement to a court for approval. It is important to consult with a legal professional to ensure the mediation agreement is legally enforceable.
Is Mediation Legally Binding?
Mediation is a popular alternative dispute resolution process that allows parties to resolve their conflicts outside of the courtroom. It involves a neutral third party, known as the mediator, who facilitates communication and negotiation between the parties. One question that often arises in the context of mediation is whether the agreements reached during the process are legally binding. In this article, we will explore the concept of legally binding mediation and shed light on its implications.
Understanding Legally Binding Mediation
Mediation is a voluntary process, which means that the parties involved have the freedom to participate or withdraw at any time. Unlike litigation or arbitration, mediation does not result in a binding decision imposed by a judge or arbitrator. However, the agreements reached during mediation can be legally binding if the parties choose to make them so.
During mediation, the parties have the opportunity to discuss and negotiate the terms of their agreement. Once they reach a mutually acceptable resolution, they can choose to formalize it in a legally binding document. This document, often referred to as a mediation agreement or settlement agreement, outlines the terms of the agreement and is signed by all parties involved. By signing the agreement, the parties indicate their intention to be bound by its terms and to enforce them if necessary.
Factors That Determine Legally Binding Mediation
While the parties have the option to make their mediation agreement legally binding, there are certain factors that can affect its enforceability. These factors may vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific circumstances of the case. Here are some key considerations:
1. Intent: The parties must clearly express their intention to be bound by the terms of the agreement. This can be done through explicit language in the agreement itself or through their actions during the mediation process.
2. Formality: In some jurisdictions, there may be specific requirements for a mediation agreement to be legally binding. This may include the need for the agreement to be in writing, signed by all parties, and witnessed by a neutral third party.
3. Consideration: Like any contract, a legally binding mediation agreement requires consideration, which refers to something of value exchanged between the parties. This can be a promise to perform certain actions, the payment of a sum of money, or any other form of consideration agreed upon by the parties.
4. Capacity: The parties involved in the mediation must have the legal capacity to enter into a binding agreement. This means that they must have the mental capacity to understand the terms of the agreement and the consequences of entering into it.
5. Public Policy: While mediation allows parties to resolve their disputes privately and amicably, there are certain limitations imposed by public policy. If the terms of the agreement violate any laws or public policy considerations, it may not be enforceable.
It is important to note that even if a mediation agreement is not legally binding, it can still have persuasive value in future legal proceedings. Courts often consider the parties’ good faith efforts to resolve their disputes through mediation and may take their agreements into account when making decisions.
In conclusion, mediation can result in legally binding agreements if the parties choose to formalize their resolution in a written document. However, the enforceability of these agreements may depend on various factors, including the parties’ intent, the formality of the agreement, the presence of consideration, the capacity of the parties, and compliance with public policy. Parties considering mediation should consult with legal professionals to understand the specific requirements and implications in their jurisdiction.
Key Takeaways: Is Mediation Legally Binding?
- Mediation is a voluntary process where a neutral third party helps resolve disputes.
- Mediation agreements are not automatically legally binding.
- However, parties can choose to make their mediation agreement legally binding by turning it into a contract.
- Mediation offers flexibility and a chance for parties to find mutually agreeable solutions.
- It is important to consult with an attorney to understand the legal implications of mediation agreements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Mediation is a popular method of resolving disputes outside of a courtroom. If you are considering mediation, you may be wondering about its legal implications. Here are some frequently asked questions about whether or not mediation is legally binding.
1. Can a mediated agreement be legally binding?
Yes, a mediated agreement can be legally binding if both parties agree to it. The agreement reached in mediation is typically formalized into a written contract that outlines the terms and conditions agreed upon. This contract can be enforceable in court, just like any other legally binding agreement.
However, it is important to note that the enforceability of a mediated agreement may vary depending on jurisdiction. It is advisable to consult with a legal professional to ensure that the agreement meets the necessary legal requirements in your specific jurisdiction.
2. What makes a mediated agreement legally binding?
A mediated agreement becomes legally binding when certain conditions are met. First, both parties must voluntarily agree to the terms and conditions of the agreement. This means that there should be no coercion or duress involved in the decision-making process.
Second, the agreement should be clear and specific, leaving no room for ambiguity. It should address all relevant issues and outline the rights and responsibilities of each party. Finally, the agreement should be signed by both parties to signify their intention to be bound by its terms.
3. Can a mediated agreement be enforced in court?
Yes, a mediated agreement can be enforced in court if one party fails to comply with its terms. In such cases, the aggrieved party can file a lawsuit to seek enforcement of the agreement. However, it is important to note that the process of enforcing a mediated agreement may vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific terms of the agreement.
In some cases, the court may treat the mediated agreement as a contract and enforce it accordingly. In other cases, the court may require the parties to undergo additional steps, such as a consent order or judgment, to make the agreement enforceable. It is advisable to consult with a legal professional to understand the specific process in your jurisdiction.
4. What happens if a mediated agreement is not legally binding?
If a mediated agreement is not legally binding, it means that the parties are not obligated to comply with its terms. In such cases, the agreement may be considered non-binding and non-enforceable in court. If one party fails to fulfill their obligations under a non-binding agreement, the other party may have limited options for seeking recourse.
However, even if a mediated agreement is not legally binding, it can still serve as a valuable tool for resolving disputes. It can help the parties identify common ground and reach a mutually acceptable solution. In many cases, parties are more likely to comply with the terms of a mediated agreement even if it is not legally binding due to the voluntary nature of the process and the desire to maintain a positive relationship.
5. Are there any alternatives to mediation that are legally binding?
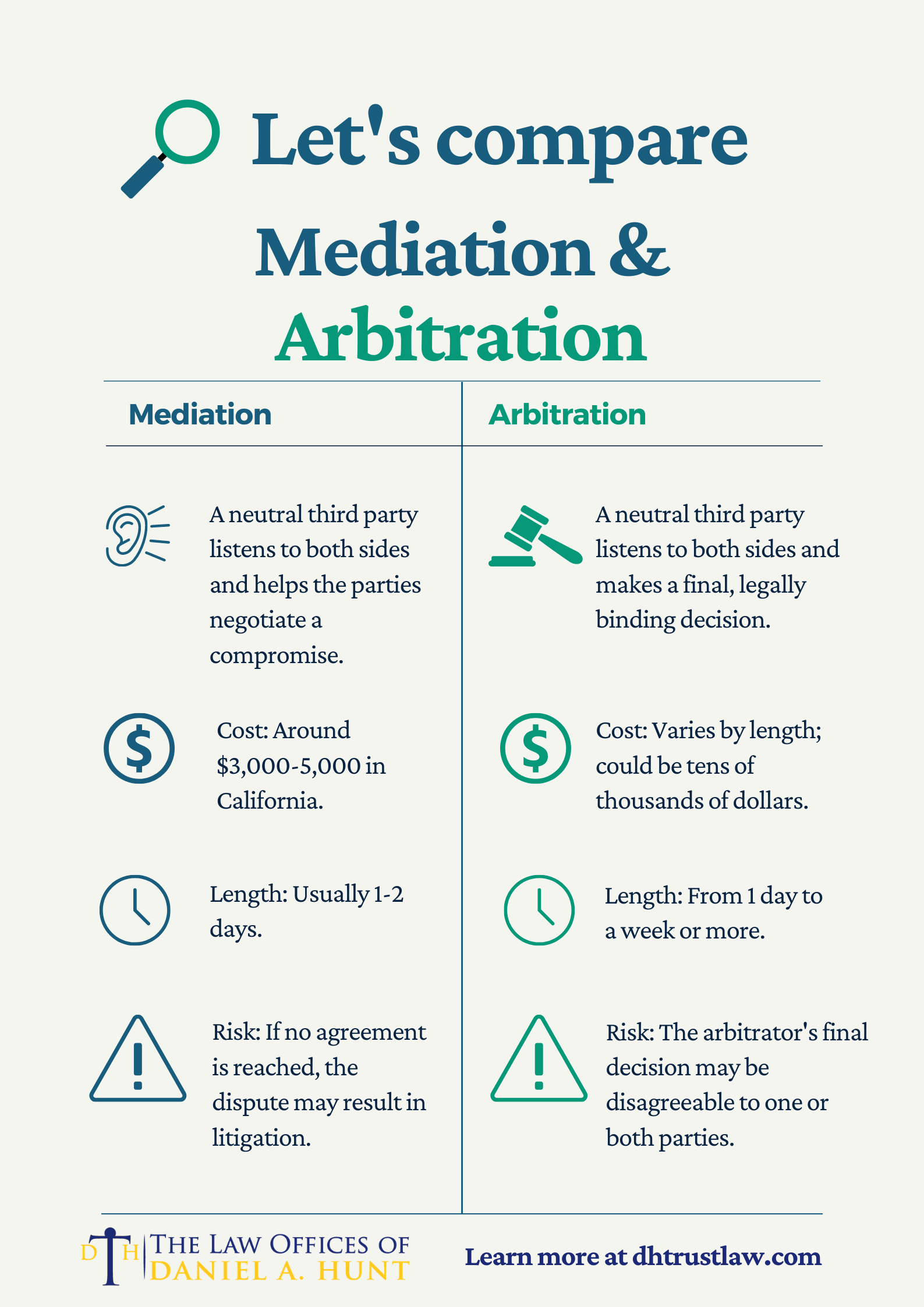
Yes, there are alternative methods of dispute resolution that are legally binding. One such method is arbitration, where a neutral third party, known as an arbitrator, hears the arguments of both parties and makes a binding decision. Unlike mediation, where the parties have control over the outcome, the decision made in arbitration is final and enforceable.
Another alternative is litigation, which involves resolving disputes through the court system. In litigation, a judge or jury makes a final decision based on the evidence and arguments presented by the parties. The court’s decision is legally binding and enforceable. However, it is important to note that litigation can be a lengthy and costly process, which is why many parties opt for mediation or other alternative dispute resolution methods.
Final Summary: Is Mediation Legally Binding?
In conclusion, while mediation offers a flexible and collaborative approach to dispute resolution, it is important to understand its legal implications. Mediation itself is not legally binding, meaning that the mediator’s decision or agreement reached during the process is not enforceable by a court of law. However, the final outcome of mediation can be made legally binding if parties choose to formalize their agreement through a legally recognized document, such as a settlement agreement or consent order.
It is crucial for individuals engaged in mediation to be aware of the legal nature of their agreement and to consult with legal professionals to ensure that their rights and interests are adequately protected. This is especially important when dealing with complex legal matters or situations where significant financial or personal consequences are at stake. By seeking legal advice and properly documenting their agreement, parties can ensure that the outcome of mediation is legally enforceable and provides them with the necessary protection and peace of mind moving forward.
Remember, while mediation can be a valuable tool for resolving conflicts, it is always wise to understand the legal implications and take the necessary steps to safeguard your rights. By approaching mediation with a clear understanding of its limitations and seeking appropriate legal guidance, you can navigate the process effectively and reach a resolution that is both satisfactory and legally binding.
