When it comes to co-parenting, understanding your legal rights regarding custody and visitation is crucial. Navigating the complexities of co-parenting can be challenging, but knowing where you stand legally can provide clarity and help you make informed decisions. So, what legal rights do co-parents have when it comes to custody and visitation? Let’s explore this topic further.
Co-parenting is a shared responsibility, and both parents have rights and responsibilities when it comes to their children. It’s essential to understand that these rights and responsibilities can vary depending on the specific circumstances and the laws of your jurisdiction. However, generally speaking, co-parents have the right to participate in making decisions regarding their children’s upbringing, including education, healthcare, and religious practices. Additionally, they also have the right to spend quality time with their children through visitation or parenting time arrangements.
Understanding the legal framework surrounding co-parenting rights is essential for creating a harmonious and stable environment for your children. By knowing your rights and responsibilities as a co-parent, you can effectively navigate the challenges that arise and ensure the best interests of your children are prioritized. Now, let’s delve deeper into the legal aspects of co-parenting, exploring various custody and visitation arrangements and how they can be tailored to suit your unique situation. So, let’s get started!
Understanding the Legal Rights of Co-Parents in Custody and Visitation
Co-parenting can be a complex and challenging journey, especially when it comes to determining custody and visitation rights. As a co-parent, it’s crucial to understand your legal rights and obligations to ensure a healthy and supportive environment for your children. This article will provide valuable information on the legal rights that co-parents have regarding custody and visitation arrangements.
1. Legal Definitions and Types of Custody
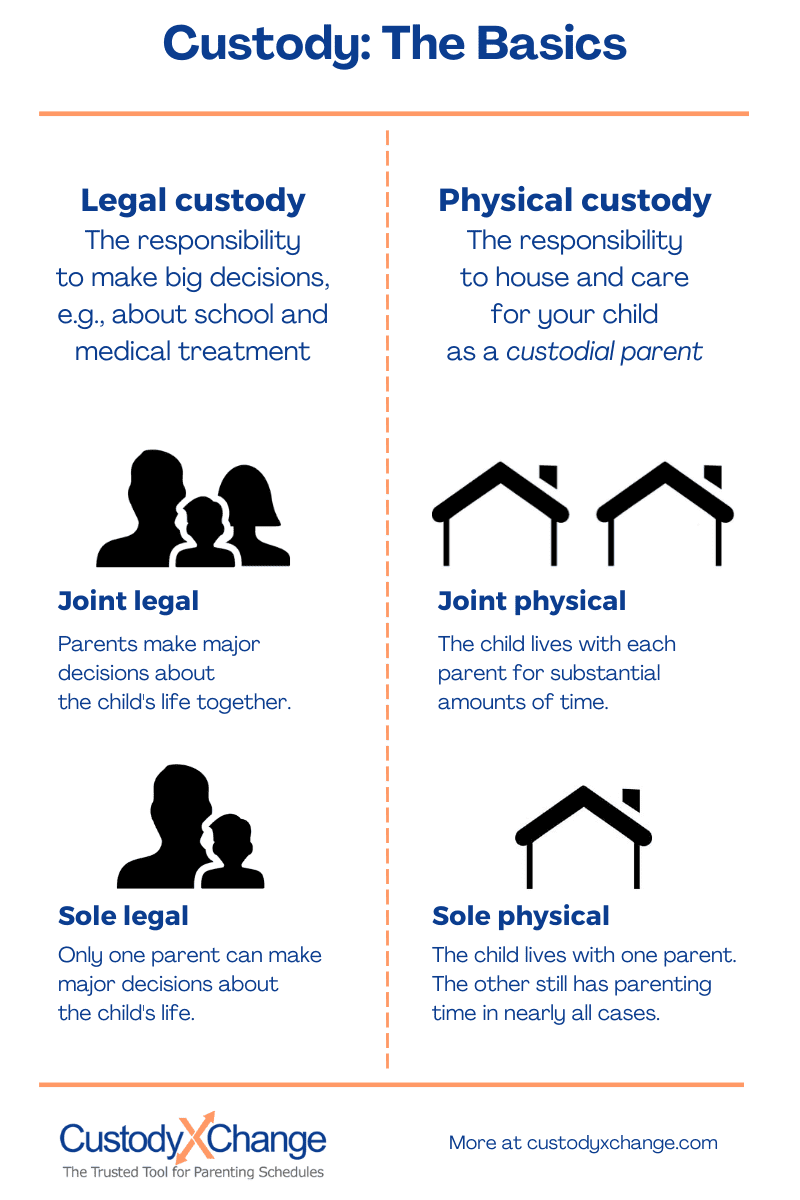
When it comes to custody, it’s essential to understand the legal definitions and different types of custody arrangements. Custody refers to the legal right and responsibility of a parent to make decisions regarding the child’s upbringing. There are two main types of custody: physical custody and legal custody.
Physical custody determines where the child primarily resides, while legal custody grants the authority to make significant decisions regarding the child’s education, healthcare, and religious upbringing. In some cases, custody can be joint, where both parents share physical and legal custody, or sole, where one parent has primary physical or legal custody.
Joint Custody
Joint custody allows both parents to have an active role in their child’s life. This arrangement can be beneficial for fostering a healthy co-parenting relationship and ensuring the child’s well-being. When co-parents share joint physical custody, the child spends significant time with both parents. Joint legal custody involves both parents making decisions together regarding the child’s upbringing.
Sole Custody
Sole custody grants one parent the primary responsibility for the child’s physical and legal care. In this arrangement, the non-custodial parent may still have visitation rights, but they do not have decision-making authority. Sole custody is typically awarded when one parent is deemed unfit or when it’s in the best interest of the child due to factors like domestic violence or substance abuse.
2. Factors Considered in Custody Determination
When determining custody arrangements, courts consider various factors to ensure the child’s best interests are met. Some common factors include:
– The child’s age and preferences (if old enough to express them)
– The physical and mental health of both parents
– Each parent’s ability to provide a stable and nurturing environment
– The existing relationship between the child and each parent
– Any history of domestic violence or substance abuse
– The willingness of each parent to support the child’s relationship with the other parent
It’s crucial for co-parents to present themselves as capable caregivers and demonstrate their commitment to fostering a healthy and supportive environment for their children.
3. Creating a Parenting Plan
A parenting plan is a crucial document that outlines the custody and visitation arrangements between co-parents. It should address various aspects, including the child’s living arrangements, visitation schedules, decision-making processes, and methods for resolving conflicts.
When creating a parenting plan, it’s essential to communicate openly and work together to find common ground. Consider the child’s needs and schedule, and be willing to compromise to ensure the plan is in their best interests. It may be helpful to seek the assistance of a mediator or consult with an attorney specializing in family law to help facilitate the process.
Benefits of a Well-Structured Parenting Plan
A well-structured parenting plan offers several benefits for both co-parents and children. It provides stability and predictability, reduces conflict, and promotes effective communication between parents. Additionally, a parenting plan can help minimize misunderstandings and disagreements, ensuring that both parents are on the same page when it comes to important decisions regarding the child’s upbringing.
4. Understanding Visitation Rights
Visitation rights refer to the non-custodial parent’s right to spend time with their child. Even if one parent has primary physical custody, the other parent typically has the right to visitation, unless it is deemed to be against the child’s best interests.
Visitation schedules can vary widely, depending on the circumstances and the child’s age. They can range from supervised visitation, where a third party is present during visits, to unsupervised visitation, where the non-custodial parent has alone time with the child. The court will determine the appropriate visitation arrangements based on the child’s best interests.
Ensuring Successful Visitation
Successful visitation requires effective communication and cooperation between co-parents. Here are some tips to ensure positive visitation experiences:
1. Respect the visitation schedule and be punctual.
2. Encourage a positive relationship between the child and the non-custodial parent.
3. Be flexible and accommodating when possible.
4. Maintain open lines of communication regarding any changes or concerns.
5. Focus on the child’s well-being and prioritize their needs during visitation.
By following these guidelines, co-parents can create a supportive and nurturing environment during visitation periods.
5. Modifying Custody and Visitation Orders
Custody and visitation orders can be modified if there is a significant change in circumstances or if the current arrangements are no longer in the child’s best interests. Common reasons for modification include parental relocation, changes in work schedules, or concerns about the child’s safety or well-being.
To modify custody or visitation orders, co-parents must typically file a petition with the court. It’s essential to consult with an attorney to navigate the legal process and understand the requirements in your jurisdiction.
In conclusion, co-parents have legal rights and responsibilities when it comes to custody and visitation. Understanding the different types of custody, factors considered in custody determinations, creating a parenting plan, and ensuring successful visitation are crucial for fostering a healthy co-parenting relationship and prioritizing the best interests of the child. Remember to consult with a legal professional for personalized advice based on your specific circumstances.
Key Takeaways: What Legal Rights Do Co Parents Have Regarding Custody and Visitation?
- Co parents have the legal right to seek custody and visitation arrangements for their children.
- The court considers the best interests of the child when determining custody and visitation rights.
- Co parents have the right to participate in decision-making regarding the child’s upbringing, education, and healthcare.
- Both parents have the right to spend quality time with their child through visitation schedules.
- If one parent violates custody or visitation orders, the other parent has the right to seek legal remedies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors determine custody and visitation rights for co-parents?
When determining custody and visitation rights for co-parents, the court takes into consideration several factors. These may include the child’s best interests, the willingness of each parent to encourage a close and ongoing relationship with the other parent, the ability of each parent to provide a stable and nurturing environment, and the child’s preferences, depending on their age and maturity. The court will also consider any history of domestic violence or substance abuse, as well as the physical and mental health of both parents.
It’s important for co-parents to be prepared to provide evidence and present their case in court. This may involve gathering documentation, such as school records, medical records, and any other relevant information that can support their position as a responsible and capable parent. Consulting with an experienced family law attorney can help co-parents navigate the legal process and understand their rights and obligations.
What rights do co-parents have regarding custody?
Co-parents generally have the right to seek both legal custody and physical custody of their child. Legal custody refers to the authority to make major decisions regarding the child’s upbringing, such as education, healthcare, and religious upbringing. Physical custody, on the other hand, refers to where the child will primarily reside.
In some cases, co-parents may share joint legal custody, where they both have equal decision-making power. Alternatively, one parent may be granted sole legal custody, meaning they have the ultimate authority in making major decisions. Physical custody can also be shared jointly or granted to one parent, depending on what is deemed to be in the best interests of the child.
What visitation rights do co-parents have?
Co-parents who do not have primary physical custody of their child typically have the right to visitation. Visitation allows them to spend time with their child on a regular basis, even if they do not reside in the same household. The specifics of visitation rights can vary depending on the circumstances and the child’s needs.
Visitation schedules can be established through a court order or through a mutually agreed-upon parenting plan. The schedule may include regular visitation, such as weekends or weekdays, as well as holiday visitation and vacation time. Co-parents are encouraged to be flexible and cooperative in developing a visitation schedule that works best for the child and allows both parents to maintain a meaningful relationship with their child.
Can co-parents modify custody and visitation arrangements?
Yes, co-parents can modify custody and visitation arrangements if there is a significant change in circumstances or if it is in the best interests of the child. Examples of significant changes may include a parent relocating, a change in work schedule, or a change in the child’s needs or preferences.
To modify custody or visitation arrangements, co-parents typically need to petition the court and provide evidence supporting the requested modification. It’s important to note that courts generally prioritize stability and the best interests of the child, so any proposed modifications should be well-reasoned and supported by compelling evidence.
What can co-parents do if one parent is not following the custody and visitation agreement?
If one parent is not following the custody and visitation agreement, co-parents have legal remedies available to enforce the agreement. One option is to file a motion for contempt of court, which can result in penalties for the non-compliant parent, such as fines or even jail time. Another option is to seek a modification of the custody or visitation agreement to address the non-compliance.
It is advisable for co-parents to document instances of non-compliance, such as missed visitation or refusal to follow the agreed-upon schedule. This documentation can be useful in court proceedings to demonstrate the pattern of non-compliance and support the request for enforcement or modification. Consulting with an attorney experienced in family law can help co-parents navigate the legal process and protect their rights and the best interests of their child.
Child Custody – A word about Father’s Rights…If she is “keeping your child away from you”
Final Thoughts
Now that we’ve explored the legal rights of co-parents regarding custody and visitation, it’s clear that these rights are crucial for ensuring the well-being of the children involved. Co-parenting can be a challenging journey, but understanding the legal framework can provide clarity and guidance for both parties. Remember, each situation is unique, and the specific rights and responsibilities may vary depending on the jurisdiction and individual circumstances.
One important aspect to keep in mind is that the best interests of the child are always the top priority in custody and visitation cases. Courts will consider factors such as the child’s age, their relationship with each parent, and the ability of each parent to provide a safe and stable environment. It’s essential for co-parents to communicate effectively, cooperate, and demonstrate their commitment to the child’s well-being.
In conclusion, co-parenting comes with legal rights and responsibilities that aim to protect the children involved. By understanding these rights and working together, co-parents can create a nurturing and supportive environment for their children. It’s important to consult with legal professionals to ensure a clear understanding of the laws and regulations in your jurisdiction. Remember, the journey of co-parenting is about putting the child first and fostering a positive and loving environment for their growth and development.
